The importance of measuring the distribution of vertical forces per wheel in static conditions for maintenance
Over the past 20 years, the European Community has become the protagonist of a succession of actions aimed at creating a single common railway area. This required the harmonisation of technical, administrative and safety standards that are essential to obtain the interoperability of the various national railway systems. The regulatory process began in 2001 with the publication of the 1st Railway Package. Currently the EU member states are grappling with the transposition of the latest directives published in the Official Journal as part of the implementation of the 4th Railway Package: the EU Directive 2016/797 “on the interoperability of the rail system within the European Union” and the EU Directive 2016/798 “on railway safety“.
On the push of the affirmation of interoperability, it was also necessary to harmonise the safety parameters of each train running within the European railway area. For this reason, during these years of the establishment of a single railway system, several EU regulations have followed, based on the continuous innovations of the railway sector. They have listed and enforced the essential requirements that a rolling stock operating on EU networks is required to comply with, depending on its category. These regulations are called Technical Specifications for Interoperability (TSI).
The following TSIs are in force for the two main categories of rolling stock:
- COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 321/2013 of 13 March 2013 concerning the technical specification for interoperability relating to the subsystem ‘rolling stock — freight wagons’ of the rail system in the European Union (TSI WAG)
- COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 1302/2014 of 18 November 2014 concerning a technical specification for interoperability relating to the ‘rolling stock — locomotives and passenger rolling stock’ subsystem of the rail system in the European Union (TSI LOC&PAS)
For both, the latest consolidated version in force is dated 11/03/2020.
The correct distribution of the weight force exerted on the rail by each wheel is one of the essential requirements that a rolling stock operating on EU networks is required to comply with. It’s a crucial parameter which comes into play during critical moments of circulation such as braking, curves and running on twisted tracks. For this reason, the static distribution of vertical forces per wheel of the same wheelset is regulated by particularly stringent limits.
Regulation 1302/2014 disciplines and takes into account the parameter of the vertical static force per wheel within the scope of two essential requirements:
- Wheel load
- Safety against derailment running on twisted track
Wheel load
The paragraph 4.2.3.2.2. of this Regulation states that:
“The ratio of wheel load difference per axle Dqj = (Ql – Qr)/(Ql + Qr), shall be evaluated by wheel load measurement, considering the load condition ‘design mass in working order’. Wheel load difference higher than 5 % of the axle load for that wheelset are allowed only if demonstrated as acceptable by the test to prove safety against derailment on twisted track[…]”
So, except in exceptional cases, the relative deviation of wheel load per axle cannot be higher than 5%.
Safety against derailment running on twisted track
The paragraph 4.2.3.4.1 of the TSI LOC&PAS states that:
“The unit shall be designed to ensure safe running on twisted track, taking into account specifically the transition phase between canted and level track and cross level deviations.”
Furthermore:
“The conformity assessment procedure is described in clause 6.2.3.3 of this TSI.”
6.2.3.3
“The demonstration of conformity shall be carried out in accordance with one of the methods specified in the specification referenced in Appendix J-1, index 83[…]”.
Table of Appendix J-1, index 83:
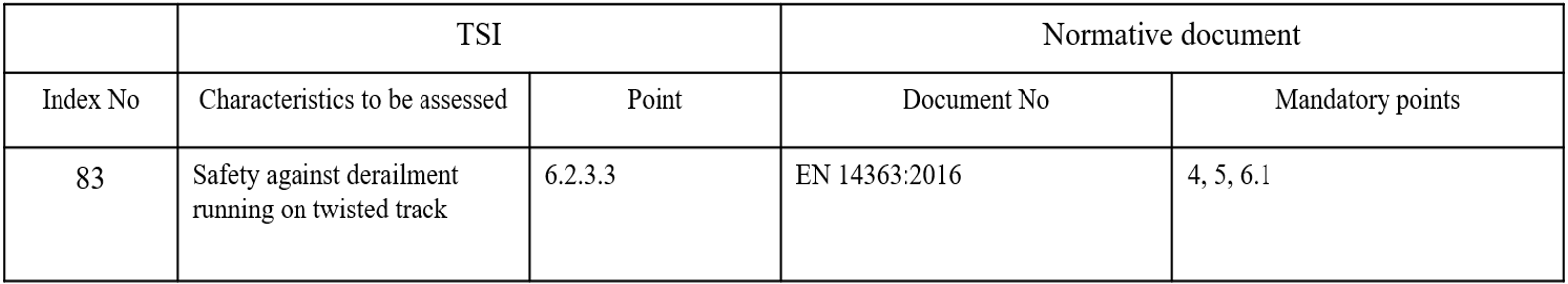
The paragraph 5.3.3 of EN 14363 provides for the measurement of the distribution of static vertical forces per wheel.
Therefore, to meet the essential requirement Safety against derailment running on twisted track, measurement of the wheel forces is required.